- Home
- MedBound Hub
- InternshipInternship
- BiographyBiography
- InterviewInterview
- Medicine
- Pharmacy
- Physical Therapy
- Biotechnology
- College/InstituteCollege/Institute
- Dentistry
- Blog
- Wellness & Nutrition
- Nursing
- Opinion
- Videos

By Dr. Himanshi Porwal
What are Dental caries?
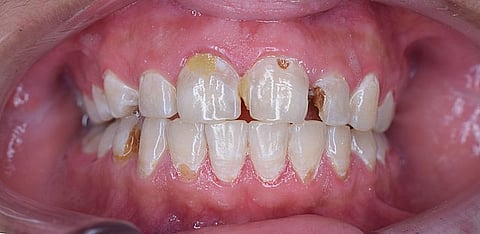
Dental caries or cavities in simple terms mean the decay of teeth or the “holes” in the tooth. The term originates from the Latin word “caries” which means decay. It is reported to be one of the oldest diseases in Man and in ancient times, it was named “tooth worm”. It mainly occurs due to the presence of bacteria named Streptococcus mutans, which has the property of getting attached to the tooth surface. Any sugar-containing substance gets converted to acid by these notorious bacteria, ultimately resulting in caries which we often see as blackish or brownish areas of discolouration on the tooth surface.
What Causes Dental Caries?
There are 1000s of bacteria that reside in our mouth and hence the occurrence of caries and other oral diseases are attributed to the presence of these bacteria and their actions on the food substances that we consume. These bacteria that are present within the mouth, are not randomly present or arranged, instead, they have a colony of themselves. The colony where these bacteria reside and act together is known as Dental Biofilm and it is this biofilm which is responsible for the initiation of caries. The dental biofilm also known as plaque is very sticky and the bacteria Streptococcus mutans is responsible for its stickiness. When any food substance containing sugar or fermentable carbohydrates is consumed, the bacteria that are living in the colonies named Dental Biofilm act on these sugars and convert them into acids which in turn snatch away all the minerals on the tooth surface and over a period lead to cavities or tooth decay which we often see as blackish or brownish spots on the tooth surface.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of caries depend on how much of the tooth surface has been involved in the decay.
● If it is in the very initial or the starting stage, it might just appear as chalky white spots on the tooth surface and the patient may complain of discolouration of the tooth surface.
● If it has progressed further and created a hole on the tooth surface, the patient might present with a complaint of food lodgment or food getting stuck between the teeth or on the surface of the tooth.
● Finally if the decay has progressed to a greater depth of the tooth surface, the patient might present with pain in the tooth or complain of pain while sleeping at night or while consuming something hot or cold.
Diagnosis of Dental caries
There are various techniques which can be used in the diagnosis or detection of Dental caries and some of them are listed below.:
● Visual-tactile method: This is the most common and the simplest physical method of evaluation of dental caries used by dentists wherein with the help of a simple explorer and a mouth mirror, the dentist checks for the presence of “catch” or any loss of tooth structure. Caries may be suspected in such cases.
● Radiographic Method: There are several radiographic techniques like Intraoral Periapical Radiograph or bitewing radiograph which are used by dentists to confirm the diagnosis and judge the severity and extent of the decay.
● There are chemical methods like Caries Detecting dyes which help in the diagnosis of caries by adding colour to the tooth structure to distinguish between the affected and the unaffected tooth structure.
What are the complications of Dental caries?
● Dental caries, if left untreated for a prolonged time, can lead to abscess formation which is a form of swelling associated with infection and the patient might present with a fever over some time.
● If the cavity affects a greater structure of the tooth, it may lead to the loss of the tooth structure and the teeth might become loose and eventually fall off.
● The root cause of cavity formation is the bacterial biofilm. This biofilm or the colony of bacteria if left untreated can lead to bleeding or swollen gums over time. ● The gum disease can further progress to the tissues that hold the tooth attached to the socket and affect them leading to infection in the area around the tooth.
Treatment of Dental Caries
The management of dental caries depends on how severe it is and how much of the tooth structure has been involved. The treatment is along the following lines:
● If the carious lesion is in the initial stage where the lost minerals of the tooth can be regained back, preventive treatment like application of fluoride gels or varnishes or pit and fissure sealants might be of great help as these materials seal the small pits on the tooth surface which are the most vulnerable sites for bacterial action and hence prevent the progression of caries.
● If the cavity is such that the patient does not present with any symptoms of severe pain, the dentist might just remove the caries with an instrument similar to a drilling machine and fill it with a suitable restorative material. There are a variety of restorative materials available, some of them have a colour similar to the colour of the tooth which are known as composites advised mainly in patients with an esthetic concern. Also, there is Silver amalgam, which is used often as a restorative material in areas where esthetics is not a major concern.
● If the cavity has extended to a large portion of the tooth structure, and if there is severe and unbearable pain, the dentist might advise you to undergo a Root canal treatment which is nothing but cleaning the tooth up to the root surface followed by placement of a dental crown or “Cap” to cover the visible portion of the tooth.
Dr. Himanshi Porwal is a passionate dentist currently working as a medical content analyst. She completed her BDS from Manubhai Patel Dental College, Vadodara. She invests her free time in reading books and travelling.
Interested in Dentistry? Read Oral cancer may be detected without biopsy
Diabetes May Weaken Teeth and Promote Tooth Decay
Join MedBound - a socio educational platform for medicos & download the app.
Take this quiz to refresh your knowledge!
