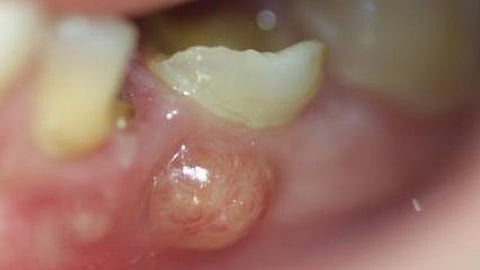
A dental abscess is defined as a bacterial infection where a pocket of pus is formed within the tooth, in the gums, or in the bone where the tooth is present. It is a very painful condition and is considered an emergency.
Types of dental abscesses
Periapical abscess
Periodontal abscess
Pericoronal abscess
Gingival abscess
Endo-periodontal abscess
Causes of dental abscess
The causes of dental abscesses vary according to their types.
Periapical abscess
Dental caries and fractures are the most common causes of periapical abscesses. Bacteria invade through the carious lesion as the disease progresses. It spreads from enamel to dentin to the pulp. When the infection reaches the pulp, it causes inflammation of the pulp called pulpitis. If not treated at this point, pulpitis can lead to a periapical abscess.
Periodontal abscess
Advanced periodontal disease is the main cause of periodontal abscess. It begins with dental plaque or calculus, which occurs due to poor oral hygiene. When the bacteria invade the gingiva or periodontium, an inflammatory response is commenced by our immune system, which results in a localized pus-filled abscess on the periodontium.
Gingival abscess
It is also known as a gum abscess and occurs due to the impingement of a sharp object or tooth bristle. They do not involve teeth and are present only in the affected part of the gingiva or gums.
Pericoronal abscess
A pericoronal abscess is found in the gums surrounding a partially or fully erupted tooth. It is commonly associated with the partially erupted third molar or wisdom tooth. It is caused when the overlying gums around the tooth become inflamed due to the collection of food and debris.
Perio-endo lesion
When the abscess is of both pulpal and periodontal origin, it leads to a perio-endo lesion, which can lead to an abscess. Dentists often find it difficult to diagnose whether it is pulpal or periodontal in origin.
Microbial flora
Streptococcus and Staphylococcus have been found to be frequently associated with dental abscesses. Various sample analyses reveal that species belonging to Fusobacterium, Clostridium, Prevotella, and Treponema are also found in dental abscesses.
Signs and symptoms
Pain
Swollen gums
Redness in the area of the abscess
Mobile tooth
Difficulty in mouth opening
Difficulty in swallowing
A bitter taste in the mouth
Bad breath
Swollen lymph nodes
Fever
How is a dental abscess diagnosed?
An oral examination is the first step in the diagnosis process. The diagnostic instrument is tapped on the infected tooth and the vestibule near the tooth. If tenderness is present on both, an abscess is suspected.
For a detailed examination, your dentist will recommend an x-ray of that particular tooth, known as an intraoral periapical radiograph (IOPAR), to determine the extent of the infection. If the infection has spread to other regions, an orthopantomogram (OPG) is advised.
In severe cases, the infection can spread to the neck or other areas. In that case, computed tomography (CT) is recommended.