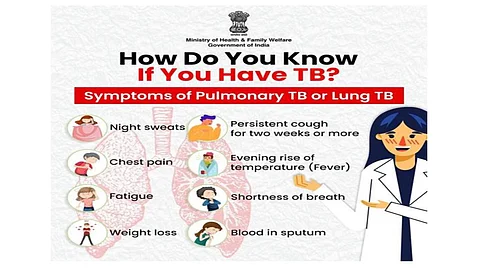

India’s dedicated journey towards tuberculosis (TB) elimination has achieved global acknowledgment, with a remarkable 17.7% reduction in TB cases between 2015 and 2023, far outpacing the global average decline of 8.3%, as reported in the World Health Organization’s (WHO) 2024 Global Tuberculosis Report. This milestone reflects the success of India’s National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), a comprehensive initiative focusing on advanced diagnosis, preventative care, and extensive patient support. Aimed at achieving TB elimination by 2025, this ambitious target positions India five years ahead of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target of 2030, as outlined in SDG 3.3, which calls for ending epidemics of diseases like AIDS, TB, and malaria.
To fulfill its commitment to “End TB by 2025,” India has set critical benchmarks under this target, including an 80% reduction in TB incidence and a 90% reduction in TB-related mortality, both relative to 2015 figures. The goal also emphasizes preventing TB-affected households from bearing catastrophic healthcare expenses. India’s pledge, initially declared by Prime Minister Narendra Modi at the “End TB Summit” in 2018, was reiterated at the “One World TB Summit” in 2023. Moreover, India reinforced its commitment to TB elimination in the Gandhinagar Declaration, a joint commitment by the Health Ministers and WHO’s South-East Asia Regional Office to end TB by 2030 in the region.
In alignment with the government’s commitment, the NTEP has been implementing the National Strategic Plan (NSP) for TB Elimination, designed to meet these ambitious goals. Substantial progress has been made through the NSP 2017-2025, which includes one of the world’s first mathematical models for estimating TB burden, helping to bridge gaps between targets and achievements.
India’s Comprehensive Approach through NTEP
Post-pandemic, India’s NTEP, aligned with the NSP, increased efforts to eliminate TB, achieving significant diagnostic milestones in 2023 with around 1.89 crore sputum smear tests and 68.3 lakh nucleic acid amplification tests, illustrating a robust commitment to accessible diagnosis across healthcare levels. Adapting to evolving medical practices, the NTEP has introduced shorter, all-oral regimens for drug-resistant TB (DR-TB), minimizing treatment delays and improving TB care quality. By targeting related health issues like malnutrition, diabetes, HIV, and substance abuse, the program has adopted a differentiated care approach for early diagnosis and patient support.
Preventive strategies have also been expanded significantly. Access to TB preventive treatment (TPT) has grown, with approximately 15 lakh beneficiaries receiving TPT, including shorter regimen options. States have shown a strong commitment to preventing TB among vulnerable groups, demonstrating a collective resolve to curb TB transmission.
The NTEP also addresses coexisting health conditions that can impact TB outcomes. Partnerships with other government departments have been established to tackle malnutrition, diabetes, and substance abuse in TB patients, providing holistic support and improving treatment outcomes.
Patient Care Enhanced with Supportive Services
Under the Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana, Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs) have distributed about Rs. 2,781 crore to around 1 crore beneficiaries to financially support TB patients. Further initiatives, including treatment supporter incentives, ASHA workers, TB champions, and Ni-kshay SAATHI (Family Caregiver Model), aim to bolster patient support systems. The launch of the Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (PMTBMBA) in 2022 marked an increased focus on community engagement in TB elimination, with over 1.5 lakh Ni-kshay Mitras committed to assisting TB patients.
The Road Ahead: Furthering Efforts to Eliminate TB
India is continuing to strengthen its TB elimination strategies by prioritizing various interventions, including:
• Conducting studies on adult BCG vaccination
• Expanding access to TPT and rolling out shorter, effective treatment regimens
• Enhancing molecular diagnostic availability with improved reporting and monitoring systems
• Decentralizing TB services to local healthcare centers, such as Ayushman Arogya Mandirs
• Building stronger community-based patient support systems through initiatives like PMTBMBA
India’s robust approach to TB elimination, backed by significant government commitment and community involvement, is driving positive outcomes in reducing TB incidence. With its focus on cross-sector partnerships, innovative diagnostics, and patient-centered care, India is on a promising path toward reaching its 2025 goal for a TB-free nation. This progress underscores India’s leadership in global health initiatives and highlights the effectiveness of collective, innovative, and community-driven approaches in addressing major health challenges.
(Rehash/Ankur Deka/MSM)
