
Menstruation also known as your period or menstrual cycle is a monthly occuring cycle, during which you shed the lining of your uterus which is noted as bleeding. (1)
This is a normal part of your reproductive system which is in the process of preparing for a possible pregnancy. it can tell a lot about your reproductive health. Heavy menstrual bleeding, or menorrhagia, can disrupt daily life and signal underlying health issues.
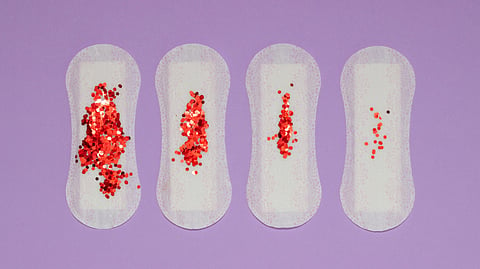
The average menstrual cycle lasts for 28 days However, it can range from 21 to 35 days and is still considered normal and lasts for around 3 - 7 days. During a typical period, you may lose between 5-80 mL of blood in total.(1)
What is menorrhagia
Menorrhagia is the term used for a heavy or long menstrual period. it is common to have a heavy flow but when longer than normal or heavier than normal periods are encountered it is considered menorrhagia and it's known to be seen in 1 of every 5 women. (3,4)
Symptoms that you must be aware of :
You may need to change your pad/tampon at least once an hour for a day or more.
You may have to change your pad in the middle of the night.
You may need to wear multiple pads to prevent a leak.
If you're passing blood clots the size of or larger than that of a quarter.
Your periods last longer than 7 days.
More than 5 tablespoons of blood is lost during your period.
Unable to do your regular activities due to your periods.
Feeling tired, or short of breath, abdominal pain/ cramps.
It is advised that if you notice any of these symptoms you should seek a consult with your health care professional. (2,3)
Menorrhagia versus metrorrhagia: menorrhagia is heavy bleeding during your periods or longer periods while metrorrhagia is bleeding between periods. (4)
MedBound Times was able to contact Dr. Jashan Chhatwal, MS Obstetrics & Gynaecology, from Karnal, Haryana who shared her insights regarding heavy menstrual bleeding. She expressed that the causes of menorrhagia could be due to Hormonal imbalance, fibroids, adenomyosis, polyps, ovulatory dysfunctions, and malignancy.
What causes menorrhagia?
Hormonal imbalances can lead to menorrhagia which could be caused due to thyroid conditions, or PCOS. Having a higher BMI than normal can also cause heavy bleeding due to interference with your body’s hormone production.
Non-cancerous growth in the uterus like Uterine fibroids, polyps, and adenomyosis.
Infections including sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can cause heavy bleeding.
if heavy bleeding is only one episode accompanied by a delayed period it could be related to pregnancy like ectopic pregnancy, or miscarriage.
Medications include warfarin, NSAIDs, aspirin, hormonal replacement therapy, IUDs, and birth control pills.
Genetic conditions like von Willebrand's disease in which the blood does not clot properly. (3)
It is pretty common to have irregular menstrual cycles during puberty. For most adolescents, surgery isn't mandatory as treatment of heavy period bleeding. you will be prescribed NSAIDs, like ibuprofen, to help with pain and reduce bleeding. They may also prescribe contraceptives, hormones, or tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss. (4)
Risk factors and Complications
Premenopausal age, obesity( BMI greater than >30 kg/m2 ), and Hormonal imbalances are some of the risk factors.
Menorrhagia can lead to serious complications as you are losing a lot of blood, it could lead to anemia, and some conditions like cancer that could be a potential reason for the bleeding should be diagnosed early on to be able to have an early intervention. (4)
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is done through a physical exam and pelvic exam, but you will also be asked in detail regarding your menstrual cycle, reproductive health and quality of life.
Apart from this, you could be asked the following :
To give a blood test to check for anemia as well as any thyroid conditions or clotting issues.
Transvaginal ultrasound or MRI to check for any abnormal growth
Pap smear to study the cells of your cervix
Cervical culture to check for infection. (3,4)
Management of Menorrhagia
Treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding depends on the underlying cause, your age, and your medical history.
For milder symptoms or causes that can be modified, such as hormonal fluctuations or conditions like overweight or obesity, lifestyle changes may be recommended.
Treatment for more severe conditions includes:
Birth control pills may be prescribed to help regulate your periods.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often suggested for heavy bleeding associated with perimenopause, though it comes with certain risks.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists and antagonists can be used to manage heavy bleeding.
Antifibrinolytic medications help prevent clots from breaking down, reducing excessive bleeding.
Iron supplements may be given to counteract anemia caused by heavy bleeding.
If medications are not effective, surgical options may be considered:
Hysteroscopy: A tube is inserted into the uterus to identify and remove the cause of bleeding.
Dilation and curettage (D&C): Removes the outermost layer of the uterine lining.
Myomectomy: Removal of fibroids from the uterus.
Uterine artery embolization (UAE): This technique restricts blood flow to fibroids and tumors.
Endometrial ablation: This procedure destroys all or part of the uterine lining.
Hysterectomy: Surgery that removes the uterus, preventing periods and pregnancy.(3)
Home remedies to alleviate symptoms
Drink plenty of water
Eat iron-rich foods like Spinach, Legumes, and Broccoli.
Increase vitamin C intake which can be found in foods like green chili peppers, guavas, yellow bell peppers Lemon, and kiwis.
Herbal teas that include cinnamon, ginger, and licorice.
Hot packs can help ease cramps, and an ice pack may reduce heavy blood flow. (5)
However, it is important to note that these remedies may not address the underlying issue. Dr. Jashan Chhatwal advises, "Do not ignore symptoms and seek help if you observe any change in their cycle." if you note any symptoms or any changes in your cycle make sure to contact a health care professional to have a proper management to your issue.
References
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/10132-menstrual-cycle(Cited on 06/08/2024)
Fraser IS, Critchley HO, Broder M, Munro MG. The FIGO recommendations on terminologies and definitions for normal and abnormal uterine bleeding. SeminTreatment depends upon severity and cause. But progestins are the mainstay of treatment Reprod Med. 2011 Sep;29(5):383-90.(Cited on 06/08/2024)
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17734-menorrhagia-heavy-menstrual-bleeding(Cited on 06/08/2024)
https://www.webmd.com/women/heavy-period-causes-treatments(Cited on 06/08/2024)
https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-stop-heavy-periods#nutrition(Cited on 07/08/2024)
MSM
